First thing first, qualitative and quantitative research are both critical in the process of conversion optimization.
One without the other makes your CRO efforts weak.
A quick Google search will show you articles prioritizing one over the other. But if you ask a CRO expert, I mean someone with optimization know-how, they will tell you that you need both.
But the question remains, do you know why you require both? Which one of the research approaches do you start with? At what stage of the conversion optimization process do you carry out qualitative research or quantitative? Is it a linear progression or a mixed model?
If you’ve got these questions and more, don’t worry, in this article, we will be looking at what is quantitative and qualitative data, the difference between qualitative and quantitative research, when to carry them out in the conversion optimization process, research methods to get the best out of qualitative and quantitative analysis, practical tips to get started and more.
Ready to begin? Let’s get started.
What is Qualitative Data?
Qualitative data describes the information and can’t be counted (expressed in numerical value).
In statistics, qualitative data is known as categorical data. This means it can be arranged into categories based on the attributes and characteristics of the interviewee.
Qualitative data answers the ‘how’ and ‘why’ question and it also gives you insight into how users think and why they act the way they do.
Examples of qualitative data.
Remember, qualitative data doesn’t include numbers in how it presents its answers and results.
1. I got the product that came in a yellow color.
2. Our customers like the green backpack.
3. This brown-colored table is our best-selling product.
What is Qualitative Research?
Qualitative research relies on collecting non-numerical data from web visitors/customers. This means you rely on opinions, observations, and motivations. With the qualitative research type, you’re asking ‘why’ questions.
Qualitative research doesn’t just help collect data; it helps you understand user trends and perspectives.
The process of carrying out qualitative research is flexible. Because it’s non-numerical in its data collection, it focuses on description rather than measurement.
Examples of Qualitative research.
1. Understanding how users perceive your product when compared to your competitors.
2. How users use your products.
What is Quantitative Data?
Quantitative data refers to every data that can be numerically quantified. If the data can be measured, quantified, counted, and has statistical value, it’s quantitative data.
Quantitative data answers the question of ‘how many, ‘how often, and ‘how much.’
Examples of quantitative data.
Remember, quantitative data is all about measurable details, quantifiable data.
1. How many visitors did we get visiting our blog this quarter?
2. By how many did our site visitors drop?
3. How many people visited our newly designed PDP page?
To make sense of quantitative data, you’ll need a statistical analysis system. This helps to evaluate the data and present it in a way to spot patterns and trends.
What is Quantitative Research?
Quantitative research is all about collecting data in numerical, measurable forms. Here, you’re not relying on opinions but going after the hard facts to explain user behavior.
Quantitative data is all about collecting numeric data and interpreting the same data.
The kind of questions you’re asking here is the ‘how’ questions.
Examples of Quantitative Research.
1. What number of times the ‘this’ call-to-action button was clicked.
2. How many visitors came from organic social?
Differences Between Qualitative and Quantitative Research
Qualitative and quantitative research complement each other; they don’t work in a silo. But that doesn’t mean they don’t differ in how data is collected, and interpreted, and the kinds of research questions asked.
| QUALITATIVE RESEARCH | QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH |
| 1. It’s often analyzed by categorizing | It’s analyzed through statistical analysis and maths. |
| 2. It’s non-numerical, it’s descriptive and mainly expressed in words. | Mainly expressed in numbers, tables, and graphs. |
| 3. Requires few respondents | Requires many respondents |
| 4. Takes time to set up. | Can be set up in a few minutes. |
| 5. It helps in forming hypotheses. | Validates theories, tests, and hypothesis |
When To Do Qualitative Research.
This should be done at the beginning of every project because qualitative research provides you with the motive, intention, and motivation of your website visitors.
Before starting any project, you want to know why your visitors act the way they do and how you can improve their experience.
It also helps in hypothesis formulation because when you discover user issues and motivations, those ideas can become hypotheses to be proven through quantitative research.
In the qualitative research approach, the audience size is small and not random, and the results you get from the qualitative research are particular and specialized, less generalizable since you worked with a sample size, not a random audience. Still, the insights you get also inform your hypothesis, which you go on and test.
Qualitative Research Methods.
Remember, qualitative research is all about collecting non-numerical data to analyze your customer behavior and better understand why they act the way they do. Here are some research methods you can employ to uncover user motivation.
1. In-depth interviews:
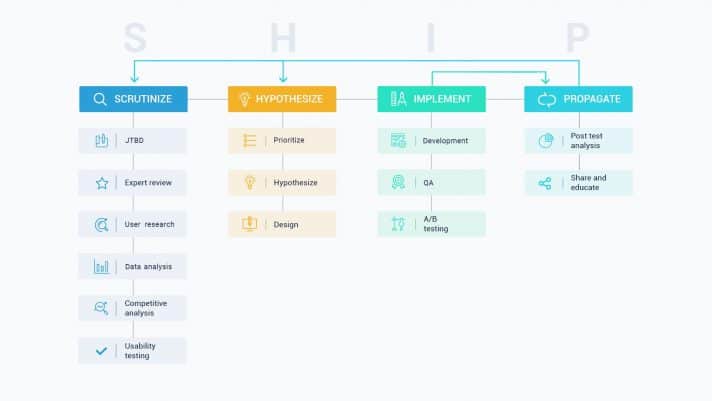
This way, you, as the researcher, get to ask web visitors questions about their experience using the website you’re working on, how easy it is, how difficult it is, do they get to find what they’re looking for or is the website derailing them? You want to ensure the person you’re interviewing is at ease with you. The JTBD framework which we use to conduct interviews fits in perfectly here. It’s part of our SHIP CRO process.
2. Open ended surveys:
3. Live Chat and Customer Service Message Analysis:
4. Remote User Testing:
This is a way of finding out how users use your website. The main aim of user testing is to discover friction in using your website. You get several users, give them a task and have them report on their experience. They all do the same job; you analyze their reports, spot a pattern, and work towards making a hypothesis.
Practical Tips For Carrying Out Qualitative Research.
While there are different approaches and types of qualitative research, it’s the most flexible approach compared to its counterpart, quantitative research. Here are a few things you should consider when carrying out qualitative research.
1. Strive for flexibility:
If you find out a specific task being carried out doesn’t give you the insights you’re looking for, there’s room to try a different approach with a new participant. Qualitative research is observant, descriptive, and non-numerical, so you have room to adjust your questions to get a different perspective.
2. Use a-speak-out protocol for remote user testing:
In remote user testing, you give users a task to accomplish on your website and get feedback from them about their experience. To make this better, have users record themselves talking out loud while interacting with your website to fulfill their task. This approach will gain you more insight than just the reported outcome they would have brought.
3. Keep your bias to yourself:
For qualitative research methods like interviews, focus groups, or open ended question surveys, avoid questions that plant ideas or lead to a certain conclusion.
You want unbiased answers from your respondents. Frame your questions in a way that doesn’t reflect your bias.
When To Do Quantitative Research.
Quantitative research helps you see the big picture. The goal is to see how users interact with your product.
Remember the hypothesis you put out during the qualitative research phase? You can validate it by looking at the numbers through statistical analysis.
It can be used to find patterns, make predictions, and generalize results for broader audience tests.
The insight you gain by analyzing the data often lets you know which page to optimize, where you’re getting the most traffic, and if your visitors are interacting with your content below the fold.
These details are only possible by analyzing heatmaps, Google Analytics, and session replays, which are quantitative research methods.
The data gathered during quantitative research helps the conversion team create benchmarks and further hypotheses to test.
Quantitative Research Methods.
Here are some quantitative research methods to get the best insight into user interactions and patterns.
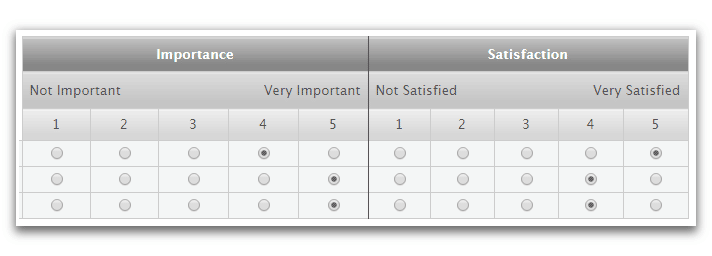
1. Rating surveys:
Quantitative research is numerical. This means the data and insight you’re getting is measured in numbers, and graphs, recorded in excel and spreadsheets. This informs the kind of survey you leave on your website. Unlike the open-ended question survey, where users get to leave comments and thoughts (which can’t be stored in numerical formats), this rating survey has numbers involved.
Here’s an example: on a scale of 1 – 5, tell us how satisfied you’re with our product. From 1 being not important and 5 being very satisfied.
2. A/B and multivariate testing:
3. Analytic tools:
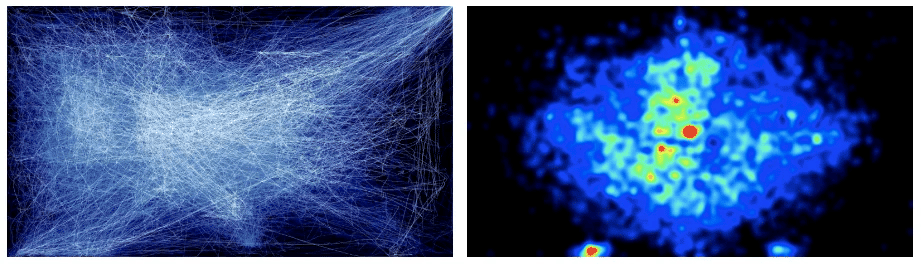
4. Mouse tracking:
This traces users’ movement on a website. This is you observing where users click and not click on your website. This also offers you insight if web visitors get below the fold on your website. Understanding how far they scroll helps you know where to put relevant content to maximize user interaction.
Practical Tips For Quantitative Research.
1. Don’t vary sessions:
Unlike qualitative research, where there’s flexibility, don’t vary the environmental conditions when studying users. To arrive at unbiased data, you need the conditions to remain true and the same for all users.
2. Invite multiple analysts to interpret the data:
When the feedback is ready, invite other analysts to see how they interpret the data. Remember, it’s numerical, a hard fact, and not subjective, so there will be differences in interpretation. This will help in improving your learning.
How To Balance Qualitative and Quantitative Research In CRO.
These two research methods don’t conflict; instead, they work better as a team.
In a conversion optimization program, the qualitative and quantitative research approach helps the conversion strategist and his team better understand why their web visitors act the way they do.
In the world of conversion rate optimization, a lot of decision-making and business strategy rests on the insights from quantitative research. Still, all that data means nothing if you don’t understand the user motivation behind them.
If I should guess, the question on your mind will be how do you work with both research methods.
You’ll most likely start with qualitative research to understand the ‘why’ for every project. The question why here informs you about the user perspective. It also helps uncover unknown competitors and motivators to your client’s business.
The next step will be to look at the quantitative data available to corroborate the information you’ve gotten from the qualitative research phase.
Quantitative research here helps to confirm every problem, data, or opportunity you were able to uncover.
Wrapping Up
The CRO process is not something that should be rushed or hurried. A mature conversion strategist knows that gathering data and doing research takes some time, and the scrutinize aspect of our SHIP process proves the amount of time we put into carrying out research.
Don’t discriminate between the qualitative process or quantitative for any project you’re working on. They are both critical. The quantitative research process provides you with the ‘what’ factor, the numerical data. It allows you to see how your users interact with your product and the friction areas.
Qualitative research helps you to understand the ‘why’ why your web visitors act the way they do, and what influences them, and this reflects in your hypothesis for the A/B test.



